
New Possibilities in Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Protein from Alaska Pollock
Research has revealed various beneficial properties of Alaska pollock protein, which is used as a raw material in products such as crab sticks, fish cake, and fried white-meat fish. While research on Alaska Pollock Protein (APP) originally began with the aim of improving blood lipids, the discovery of its muscle-increasing effects--particularly on fast-twitch muscles--has attracted attention as health consciousness grows. As the mechanisms behind muscle growth effects become clear and evidence of effectiveness in human trials accumulates, the concept that "Alaska pollock fast-twitch muscle increases human fast-twitch muscle" has gained reliability, leading to various applied research and educational initiatives.
Source: Figures based on Biomedical Research 2010, 31(6), 347-352 and J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68(2), 141-148
Figure 1. Muscle growth effects confirmed in animal experiments
Research Approach
Studies involving various proteins besides Alaska pollock confirmed that the fast-twitch muscle increasing effect is unique to Alaska pollock protein.

Source: Figure based on Nutraceuticals 2023, 3(4), 513-528
Figure 2. Evaluation results of calf muscle mass in animals after one week of material administration
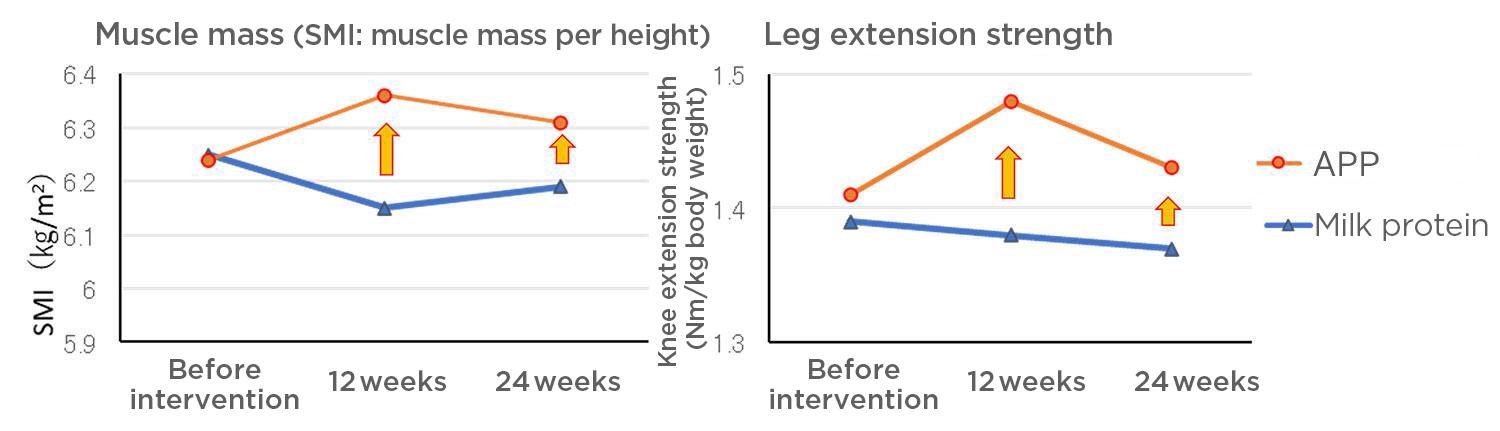
To verify effectiveness in humans, rigorous basic research was conducted. Women aged 65 and older consumed 4.5 grams of Alaska pollock protein daily for three months. While this age group typically loses about 0.5% muscle mass over three months, 15 out of 19 participants maintained or increased their muscle mass.
Additional trials have shown muscle mass increases across various age groups, including ages 16-22, 23-64, and healthy elderly individuals 65 and older.

Source: Figure based on J. Nutr. 2023, 152(12), 2761-2770
Figure 3. Results of continuous intake of 4.5g fast-twitch protein in 92 women aged 65 and older
Focus on Joint Research and Educational Activities with Research Institutions
This research began in 2009 with Ehime University, and in March 2018, the APP Research Group was established to conduct joint research with 18 universities and research institutions, including Ehime University, the University of Tokyo, Waseda University, and Tokushima University. Part of the related research has been selected for the Cabinet Office SIP (Strategic Innovation Program Research Project No. 14533567) "Next-Generation Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Creation Technology" (commissioned research by the BRAIN:Bio-oriented technology Research Advancement InstitutioN).
Furthermore, in 2020, we signed a comprehensive cooperation agreement with Tomi City, Nagano Prefecture, and started joint research with the Public Interest Foundation Institute of Physical Education Medicine targeting city residents. We are also conducting community contribution activities, such as providing the same menus as athletes to local elementary and middle schools.
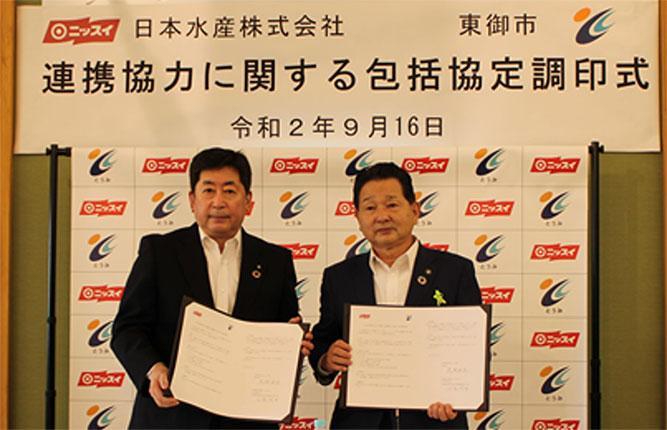
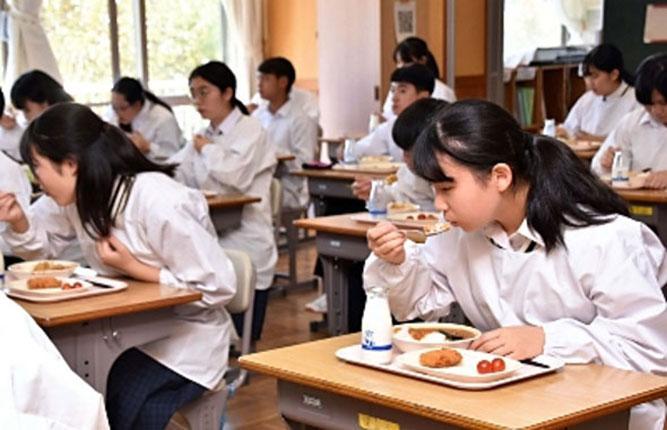


Figure 4: Examples of initiatives with Tomi City, Nagano Prefecture
In this age of centenarians, maintaining and strengthening fast-twitch muscles is crucial for preserving independence as we age. We hope to see these technological advances become part of daily life, enabling more people to maintain an active and energetic lifestyle well into their later years.
